Injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing methods for producing plastic components with high precision and repeatability. From consumer electronics to automotive parts, this process forms the foundation of modern product design and large-scale production.
Injection molding machines melt plastic materials and inject them into molds where they cool and harden into finished shapes. The result is consistent, durable, and cost-efficient production — ideal for industries like packaging, healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods.
Whether it’s a custom plastic injection molding project near you or a fully automated electric injection molding machine setup, the technology ensures precision and flexibility across a variety of materials and designs.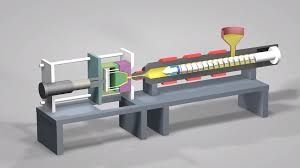
How Injection Molding Machines Work
The injection molding process involves four main stages:
-
Clamping: The two halves of the mold are securely closed.
-
Injection: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure.
-
Cooling: The material solidifies and takes the shape of the mold.
-
Ejection: The finished part is pushed out, and the cycle repeats.
Modern systems incorporate digital controls, real-time monitoring, and automation to enhance speed, accuracy, and quality.
Types of Injection Molding Machines
| Machine Type | Description | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Injection Molding Machine | Uses hydraulic pressure to inject molten plastic. Known for power and versatility. | Automotive, industrial tools |
| Electric Injection Molding Machine | Operates with electric servo motors for energy efficiency and precision. | Medical devices, electronics |
| Hybrid Injection Molding Machine | Combines hydraulic power with electric precision. | Large-scale production runs |
| Babyplast Injection Molding Machine | Compact, benchtop model for small parts or prototype runs. | R&D, dental, and micro-components |
| Custom Injection Molding Systems | Tailored machines designed for specific products or materials. | Specialized industrial parts |
Custom Plastic Injection Molding Services
Custom injection molded parts are designed based on client specifications, including size, material, tolerance, and surface finish. These services cater to low-volume prototypes and high-volume production alike.
Benefits of Custom Plastic Injection Molding:
-
Material Flexibility: Compatible with ABS, nylon, polypropylene, and more.
-
Design Accuracy: Complex geometries achievable with precision molds.
-
Scalability: Suitable for both small and mass production runs.
-
Reduced Waste: Recyclable plastic sprues and runners minimize material loss.
-
Consistency: Uniform part quality and dimensions across batches.
Key Components of an Injection Molding Machine
-
Hopper: Holds and feeds raw plastic granules.
-
Heater Barrel: Melts the plastic through controlled heat.
-
Screw and Nozzle: Push molten material into the mold.
-
Mold Unit: Determines the part shape and texture.
-
Clamping System: Ensures mold halves stay closed during injection.
-
Control Unit: Automates temperature, timing, and pressure settings.
Electric vs. Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
| Feature | Electric Machine | Hydraulic Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High (saves up to 70%) | Moderate |
| Precision | Excellent | Good |
| Maintenance | Low | High |
| Noise Level | Quiet | Noisy |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Medical, electronics | Heavy industrial |
Electric injection molding machines have become popular due to energy efficiency, speed, and cleanliness — especially in sectors demanding tight tolerances like medical or optical components.
Injection Mold Manufacturing: The Backbone of the Process
Injection mold manufacturing is a critical step that determines the shape, surface, and quality of molded products.
Steps in Mold Manufacturing:
-
Design: CAD modeling based on product requirements.
-
Tooling: CNC machining and EDM used to form mold cavities.
-
Polishing and Assembly: Ensures smooth surfaces and proper fit.
-
Testing: Sample runs check for accuracy and performance.
Molds are typically made from hardened steel, aluminum, or beryllium copper, depending on production volume and precision needs.
Applications of Injection Molding Technology
-
Automotive Industry: Dashboard components, bumpers, and interior trims.
-
Consumer Goods: Packaging, toys, and kitchenware.
-
Electronics: Housings, connectors, and cable insulators.
-
Medical Devices: Syringes, surgical tools, and lab containers.
-
Construction: Fasteners, seals, and pipe fittings.
Advantages of Injection Molding for Manufacturers
-
High Efficiency: Fast cycle times and automation reduce costs.
-
Precision Engineering: Perfect for tight tolerance requirements.
-
Material Variety: Supports thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers.
-
Reusable Scrap: Excess material can often be reprocessed.
-
Scalable Production: Suitable for thousands to millions of identical parts.
Trends in Injection Molding Technology (2025 and Beyond)
-
Smart Mold Monitoring: Sensors track real-time temperature and pressure.
-
AI-Based Defect Detection: Early prediction of inconsistencies in production.
-
3D-Printed Mold Inserts: Lower cost and faster prototyping.
-
Eco-Friendly Materials: Bio-based plastics replacing petroleum-based polymers.
-
Micro-Injection Molding: For small, intricate medical and electronic parts.
Practical Tips for Choosing the Right Injection Molding Machine
-
Determine product size and volume needs.
-
Match clamping force to mold requirements.
-
Select compatible materials (ABS, PP, PVC, etc.).
-
Evaluate energy efficiency and automation features.
-
Ensure local support for parts and maintenance.
-
For prototypes, consider compact Babyplast machines.
Conclusion
Injection molding remains a cornerstone of modern manufacturing — offering versatility, scalability, and high precision. From custom injection molded parts to fully automated electric molding systems, the technology continues to evolve toward smarter, cleaner, and more efficient production.